Choosing a Portable Generator: Key Features, Safety Tips, and Power Needs
Understanding Portable Generators
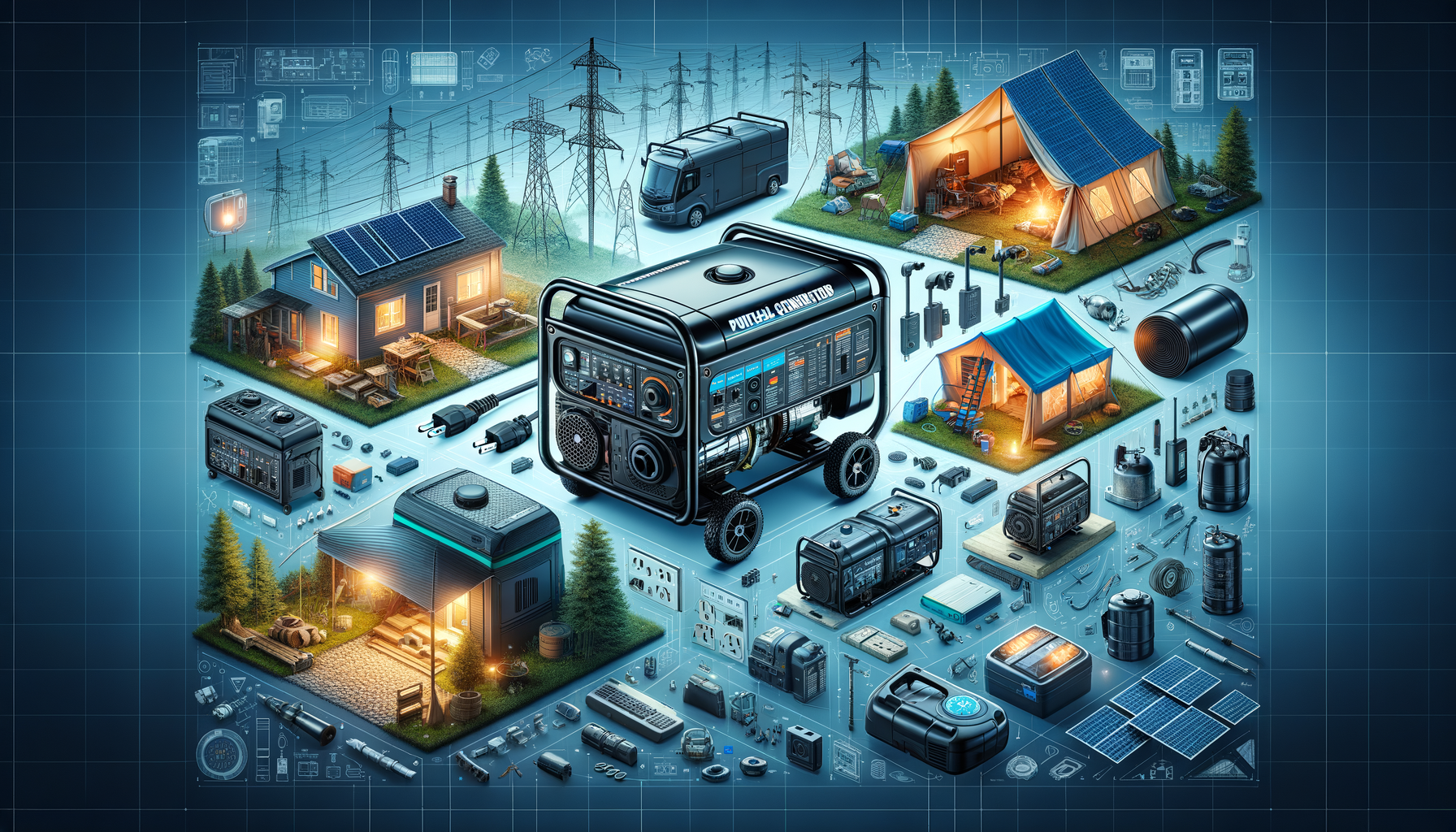
Portable generators are an invaluable asset for providing electricity during power outages or in remote areas where conventional power sources are unavailable. These versatile machines convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, offering a reliable backup power solution for homes, businesses, and outdoor activities. With various models available, selecting the appropriate generator requires a thorough understanding of your specific needs and the generator’s capabilities.
Typically, portable generators are powered by gasoline, diesel, or propane, each with its own advantages and considerations. Gasoline is widely available and easy to use, making it a popular choice for many users. Diesel generators, on the other hand, are known for their fuel efficiency and durability, especially in demanding environments. Propane offers a cleaner-burning option and is often praised for its long shelf life, making it ideal for infrequent use.
When selecting a portable generator, consider the power output you need. Generators are rated by wattage, with smaller models offering around 1,000 watts and larger units providing up to 10,000 watts or more. To determine your requirements, list the appliances and devices you intend to power and calculate their combined wattage. This will help ensure that you choose a generator capable of handling your power demands without overloading.
Key Features to Consider
Choosing the right portable generator involves evaluating several key features that can influence its performance and usability. One critical aspect is the generator’s power output, measured in watts. Consider both the starting watts, which are necessary to start appliances, and the running watts, which are needed to keep them operating.
Another important feature is the generator’s runtime. This refers to how long the generator can operate on a full tank of fuel. Longer runtimes mean fewer interruptions for refueling, which is particularly beneficial during extended power outages. Additionally, noise level is a significant consideration, especially if you plan to use the generator in residential areas or during camping trips. Look for models with noise-reducing features to ensure a quieter operation.
Portability is also a crucial factor. While all portable generators are designed to be moved, their weight and size can vary significantly. Consider models with wheels and handles for easier transportation. Furthermore, advanced features such as remote start, fuel gauges, and multiple outlets can enhance convenience and flexibility.
Safety Tips for Using Portable Generators
Safety is paramount when operating a portable generator. Improper use can lead to dangerous situations, including carbon monoxide poisoning, electrical hazards, and fire risks. To minimize these dangers, adhere to the following safety guidelines.
First, always operate your generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and vents. Carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas produced by generators, can accumulate indoors and pose a serious health risk. Installing battery-operated carbon monoxide detectors in your home can provide an additional layer of safety.
Secondly, use heavy-duty extension cords that are rated for outdoor use to connect appliances to the generator. Ensure that the cords are free from cuts or damage and are of adequate length to reach your devices without creating trip hazards.
Additionally, never attempt to backfeed power into your home’s electrical system by plugging the generator into a wall outlet. This practice is extremely dangerous and can result in serious injuries or damage to your electrical system. Instead, consider installing a transfer switch, which safely connects the generator to your home’s electrical panel.
Fuel Options and Their Implications
Choosing the right fuel type for your portable generator is essential, as it affects the generator’s performance, cost, and environmental impact. Gasoline is the most commonly used fuel due to its availability and ease of use. However, it has a shorter shelf life and can degrade over time, especially if not treated with a stabilizer.
Diesel fuel is another option, known for its energy efficiency and longevity. Diesel generators typically have a longer lifespan and can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for industrial applications. However, diesel can be more expensive and less environmentally friendly compared to other fuels.
Propane is a cleaner-burning alternative that produces fewer emissions, making it an environmentally friendly choice. It also has an indefinite shelf life, which is advantageous for infrequent use. However, propane generators generally require larger storage tanks, which can be less convenient for transport.
Ultimately, the choice of fuel depends on your specific needs and priorities, including cost, availability, and environmental considerations. Evaluate each option carefully to determine which fuel type aligns best with your requirements.
Determining Your Power Needs
Accurately assessing your power needs is crucial when selecting a portable generator. Begin by making a list of the essential appliances and devices you need to power during an outage. Common items include refrigerators, lights, heaters, and electronic devices.
Next, calculate the total wattage required by these appliances. Most devices have labels indicating their power consumption in watts. Remember to consider both the starting and running watts, as some appliances require more power to start than to run continuously.
Once you have determined your total power needs, choose a generator with a wattage rating that exceeds this amount to ensure it can handle the load. It’s advisable to select a generator with a capacity of at least 20% more than your calculated needs to accommodate additional devices or unexpected power surges.
By carefully evaluating your power requirements, you can select a portable generator that provides reliable and efficient power when you need it most.